According to medical statistics, many middle-aged women suffer from pain in the lower abdomen.This symptom is often accompanied by a disruption in normal blood circulation.This pathology is observed in many gynecological diseases, including varicose veins of the pelvis in women.Vascular problems are a very common disease.Varicose veins in the pelvic area are predominantly found in women between the ages of 25 and 50.
What are varicose veins in the pelvis?
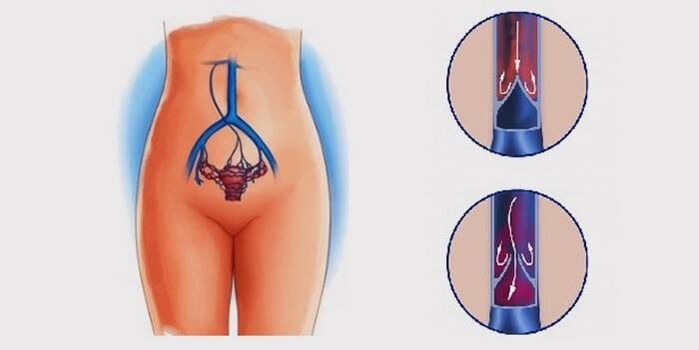
In women, every organ of the pelvic region is affected by pelvic varicose veins.The reproductive system is located in this part of the body, so the frequent development of venous pathologies can be easily explained.The pelvic vessels expand.Veins compress nerve endings and cause pain.Venous diseases are classified according to forms and stages.
Forms and degrees of severity of the disease
Varicose veins are divided into the following forms:
- The primary type of varicose veins is an enlargement of the blood vessels in the pelvis.The cause is valvular insufficiency of two types: acquired or congenital.
- The secondary form of thickening of the pelvic veins is diagnosed exclusively in the presence of gynecological pathologies (endometriosis, neoplasms, polycystic disease).
Varicose veins in the pelvic area develop gradually.There are three stages in the development of circulatory disorders in the pelvic organs:
- The veins of the organs in the pelvic area expand to a diameter of 5 mm.
- The second stage of venous enlargement is characterized by the presence of veins that “grow” up to ten millimeters.They surround the ovary on the left side.
- The third stage of varicose veins is a vessel diameter of more than 10 mm.Enlargement of veins is noted in the right ovary.In diameter it approaches the one on the left.
Why do the pelvic veins dilate?
Varicose veins of the pelvic organs occur in women for many reasons.The main prerequisites for the occurrence of circulatory failure are blockage of the veins or impaired blood flow to the ovaries.The venous trunk often becomes blocked.The blockage leads to the formation of a backup pathway for blood circulation.Varicose veins are also caused by the following factors:
- heavy physical activity;
- repeated pregnancy and labor;
- Prolonged sitting activity also leads to the formation of varicose veins.
- various gynecological ailments: inflammation of the ovaries, backward curvature of the uterus, endometriosis and chronic diseases, including;
- Disturbances in the menstrual cycle;
- Varicose veins are caused by high estrogen levels;
- Contraception from pregnancy onwards using PPA (interrupted sexual intercourse), the woman does not reach orgasm;
- Varicose veins of the pelvic organs can be caused by treatment with medications containing hormones.
Varicose veins in the pelvis during pregnancy
Problems with venous circulation in the pelvic area are not uncommon in pregnant women. They arise due to a hereditary predisposition as a result of hormonal changes.Another “incentive” for varicose veins can be the characteristics of the female body.In addition to the main causes of ART during pregnancy, there are several other factors:
They arise due to a hereditary predisposition as a result of hormonal changes.Another “incentive” for varicose veins can be the characteristics of the female body.In addition to the main causes of ART during pregnancy, there are several other factors:
- increased internal pressure in the veins due to increasing load;
- the growth of the child and, as a result, the expansion of the uterus;
- Vein dilatation occurs due to low physical activity, which is typical for many pregnant women.
Signs of varicose veins
Varicose veins in the pelvis have specific symptoms.Common signs of vasodilatation in women include:
- Severe intermittent or constant pain.It often becomes more intense during menopause or after ovulation.
- Vaginal discharge: colorless or slightly white.
- Irregularities in the menstrual cycle also indicate varicose vein thickening of the female pelvic organs.
- Increased sensitivity of the skin in the perineum, sensitivity of the vaginal mucosa.
- Pain in the last stages of pregnancy, during sex or towards the end of the day.
- Feelings of heaviness and pressure in the pelvic area are another possible symptom of varicose veins.
- Varicose veins cause slight swelling of the vagina and vulva.
diagnosis
Detection of the manifestations of varicose veins is carried out using various techniques.Diagnostic measures for varicose veins of the pelvic organs focus on two tasks:
- Conducting an examination, making a differential diagnosis - confirming varicose veins;
- To make the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to identify the area where reflux occurs (reverse reflux of venous blood).
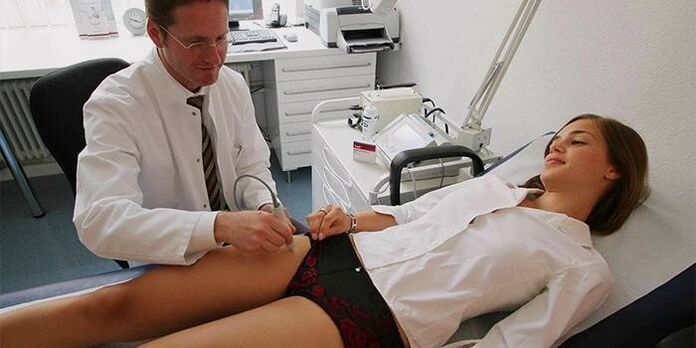
Therefore, the diagnosis of dilated veins in the pelvic organs includes the following procedures:
- Standard vaginal examination by a gynecologist.
- Ultrasound (ultrasound examination) allows you to detect the condition of the ovaries, uterus and bladder and find out whether a woman suffers from URVMT.
- Dopplerography is a study that helps determine the nuances of blood circulation in the vessels in the pelvis.
- Phlebography is a diagnostic procedure that identifies areas where blood clots form.
- Laparoscopy and computed tomography.Prescribed when definitive confirmation of varicose veins is required.
Treatment
The diagnosis and treatment of varicose veins is carried out by a phlebologist and vascular surgeon.It is recommended to combine medications to relieve varicose veins in women with therapeutic exercises and traditional medicine.VRVT therapy includes several important points:
- Elimination of backflow of venous blood;
- relief from symptoms of illness;
- stabilization of vascular tone;
- Improving blood circulation in tissues.
Medication
Medication for varicose veins must be taken in courses.The other medications that act as painkillers should only be taken during a painful attack.For effective therapy, the doctor often prescribes the following medications:
- phleboprotectors (Rutozid and others);
- enzyme preparations;
- Drugs that relieve inflammation in varicose veins (ibuprofen, ketoprofen);
- Tablets to improve blood circulation (pentoxifylline).
Surgical
Sometimes surgery is required.For example, if the symptoms of varicose veins persist for a long time and the disease develops.The doctor refers the patient for surgery.There are several types of procedures that help get rid of varicose veins:
- embolization of veins in the ovaries;
- plastic surgery of the uterine ligaments;
- removal of enlarged veins by laparoscopy;
- Compression of the veins in the pelvis with special medical clamps (clipping);
- Crossectomy - vein ligation (prescribed if, in addition to the pelvic organs, the vessels of the lower extremities are also affected).
Folk remedies
In individual cases, varicose veins of the pelvic organs are treated with conventional medicine. However, this approach will be effective only in certain circumstances: when varicose veins are detected at the very beginning of their formation and the doctor assumes that the “grandmother's” advice will not affect drug therapy.Here are some good recipes recommended for treating varicose veins of the pelvic organs:
However, this approach will be effective only in certain circumstances: when varicose veins are detected at the very beginning of their formation and the doctor assumes that the “grandmother's” advice will not affect drug therapy.Here are some good recipes recommended for treating varicose veins of the pelvic organs:
- You need to steam 1 table with a glass of hot water.a spoonful of dandelion roots.Infuse the pelvic vein varicose vein medicine for two hours.Drink 50 ml four times a day.
- Take 100 grams of chopped chestnuts.Pour in alcohol and vodka (half a liter).Leave it for a few weeks.Drink 20 drops of infusion three times a day.
- Prepare freshly squeezed carrot juice (100 ml).Add a teaspoon of oil (preferably flaxseed).Take the mixture daily in the morning.
Therapeutic exercise
It is recommended to combine medical and traditional therapy with special therapeutic exercises and wearing compression underwear.Breathing exercises for varicose veins, in which deep, slow inhalations and exhalations are carried out one after another, will not be superfluous.The system of physical activity for the treatment of varicose veins in women consists of exercises:
- "Bicycle."We lie on our backs, put our hands behind our head or place them along our body.By lifting our legs, we make circular movements with them, as if we were pedaling a bicycle.
- "Birch".We sit face up on any hard, comfortable surface.Lift your legs and gently move them behind your head.Support your lumbar spine with your hands and place your elbows on the floor.Slowly straighten your legs and lift your body.
- "Scissors".Starting position: on your back.Raise your closed legs slightly above the floor.We spread the lower limbs to the sides, bring them back and repeat the procedure.
Possible complications
Why are varicose veins in the pelvis dangerous?The following consequences of the disease are often recorded:
- Inflammation of the uterus and its appendages;
- uterine bleeding;
- bladder dysfunction;
- Formation of venous thrombosis (low percentage).
Prevention
In order for varicose veins in the small pelvis to disappear as quickly as possible and to avoid relapses of the pathology of the pelvic organs in the future, you should adhere to simple prevention rules:
- perform gymnastic exercises daily;
- prevent constipation;
- Follow a diet that must contain plant fiber.
- do not stay in one position for a long time;
- take a contrast shower of the perineum;
- To prevent the appearance of varicose veins, it is better to wear only comfortable shoes and clothing.